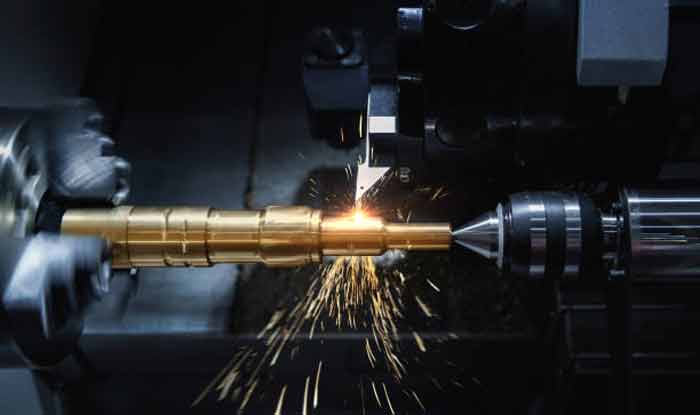
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned veteran, there are a few things you should know to make your CNC work more smoothly. For starters, you must be sure to wear work gloves on the top of the machine and in the turret. These chips will be sharp and can cause lacerations if not handled properly. Additionally, you should avoid running your CNC while you’re talking. Put the conversation on hold, and REFOCUS on the work at hand.
Choosing the right cutting tool material
The selection of cutting tools is an important decision when making a CNC turning project. Choosing the right material for tooling depends on the type of workpiece material. For instance, hardened H1 to H4 materials require lower cutting speeds and deeper cuts. A rigid setup is also recommended. Kennametal provides different material descriptions than Seco Tools. In either case, the basic criteria for selecting the right tooling is the same. Hardness, microstructure, and carbon content all determine the cutting tool’s machinability.

Choosing the right cutting tool material for your CNC turning project requires understanding the different types of materials and their properties. While ABS and nylon are both highly resistant to corrosion and have similar mechanical properties, they differ in their cutting properties. Nylon is stronger and easier to work with than ABS, but it is less polished than ABS and is poor electrical conductor. Therefore, it requires special cutting tools to avoid damage. Meanwhile, nylon is a versatile and low-friction thermoplastic material. Its rigidity, impact-resistant properties, and chemical resistance make it an excellent choice for machining parts. While Nylon is strong and durable, it can be affected by moisture, and it can be more difficult to maintain dimensional stability.
Choosing the right processing conditions
Choosing the right processing conditions for better CNC-turning processes is important in several ways. Depending on the type of material, the correct processing conditions can improve the accuracy of the CNC-turned part. While some materials are better suited for turning than others, it is necessary to consider the end use of the finished part before selecting the appropriate CNC processing conditions. For instance, if the part is to be used to make a rigid stainless steel component, the processing conditions should be different than those for a soft material such as HDPE, polycarbonate, and brass.
The first step in CNC-turned parts is creating a CAD file. This enables the manufacturing engineer to test the part’s productivity before committing to it. The CAD-CAM software makes it easier to visualise the entire process, including the raw material quality. Moreover, it allows the manufacturing engineer to choose the right parameters for the process, such as material type and size. This way, the design engineer can make the parts that meet all the specifications of the project.
Choosing the right machine tool
Selecting the right machine tool for CNC turning is crucial to achieving the desired results. You should choose a tool based on the materials you need to machine. Consider how large your parts are and whether they require off center drilling or machining on both sides. Also, consider whether you need extra support for long parts. Small parts, or those made of softer materials, should be machined at higher rpm.
The tool’s geometry will be based on the characteristics of the machining area. If the workpiece is made of a hard material, a tool with a large diameter will be most efficient. If the material is thin, it will be difficult to machine. In this case, a tool with a low aspect ratio will be better suited. Also, make sure that the centripetal angle of the tool’s center-cutting edge is high, as this will reduce cutting force. Copper, for instance, should be processed with end mills that have at least four teeth. Lastly, consider the size of the tool.